“What makes a digital product easy to use?”
Well, it’s the same thing that makes all software projects successful:
Quality UX/UI design.
Since positive user experience with software products is essential to success, having a qualified UI/UX designer is equally important. In this post, let’s talk about UI and UX designers: their responsibilities, skills, and overall role in software development projects.
Go to content sections:
- Who is UX/UI designer
- What does UX/UI designer do
- Key skills of UX/UI designers
- How to work with UX/UI designers (for business owners)
Looking for reliable UX designers? Reach out to a company with a 4.9 rating on Clutch. We know how to meet your exact needs.
What Is A UX/UI Designer?
First of all:
User experience (UX) and user interface (UI) are two different but interdependent terms. UX deals with the overall experience with a software product (how easy it is to understand and use) while UI is concerned with how the product looks and functions.
Consequently…
UX designer is responsible for making software products easy to use. To create that optimal experience, this position researches the needs of the target users and ensures they can achieve their goals with minimum effort.
UI designer creates all the screens that users use to interact with a software product. Their main task is to ensure that the visual elements conform to the needs of users as discovered by UX designers.
UX and UI designers work together to ensure that users can achieve their goals quickly and effortlessly. Their responsibilities overlap often, so many companies choose to combine the two roles into one position: UI/UX designer.
What Does a UX/UI Designer Do?
A UX/UI designer’s roles and responsibilities lie in the development, design, usability, functionality, and marketing of software products. This person is constantly involved in the creation of digital products and looks for opportunities to make them more user-friendly.
Here are the main UI/UX designer roles and responsibilities.
Target user research
Target users are the people who will be using your software. Researching their needs, goals, and problems is a must to ensure the usefulness and value of the digital product.
That’s why businesses often help UI/UX designers by giving them customer research and other data. Still, UI/UX designers conduct their own research. They conduct various kinds of usability tests to define the behaviors and goals of users.
Example:
Individual testing can reveal that users of a video streaming app prefer to search for characters rather than video titles. So, adding a function to show images of characters while typing in a search bar should increase user engagement.
Development of user persona
A user persona is a research-based description of an ideal user of a software product. The description contains helpful information for product design, including demographic data, goals, motivations, needs, values, and experience using similar products.
The purpose of creating user personas is to understand who target users are, what they are trying to achieve, what drives their behavior, and why they make buying decisions.
UI/UX designers employ these methods to create user personas:
- Online surveys
- In-person and phone interviews
- Analysis of customer research provided by clients
A typical user persona for a software product looks like this.

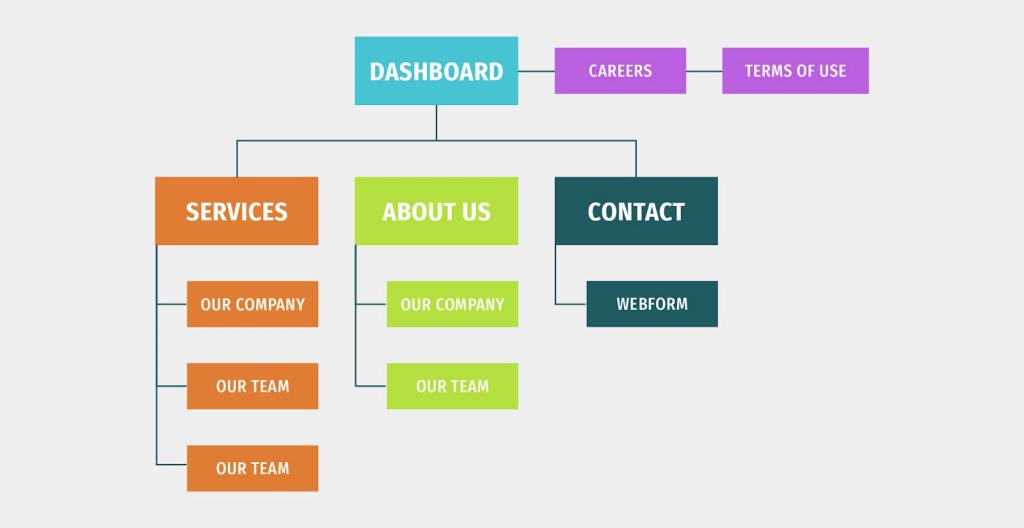
Creation of information architecture for the product
Information architecture is the way the content within a digital product is organized to guide the users to accomplish their goals. For UI/UX designers, developing information architecture is the step that follows creating user personas.
To organize and structure the content of the future digital product, UI/UX designers need to have a good understanding of the experiences, needs, and expectations of users. This understanding drives content selection.
For example, here’s a structure of a simple website of a B2B company. The most important parts of this structure achieve a goal of explaining the services and the expertise of the company to potential customers.
Wireframing
Wireframing is the practice of designing a basic structure of digital interface. UX designers create them to visualize the future digital product and establish the initial structure of interfaces. For example, a wireframe of a website page might contain its content, layout, and menu buttons.
A common way to think about wireframes is the skeleton. Thanks to them, the product takes shape, but lacks content, “the muscle,” if you will. As a client, you will be involved in the review and improvement of wireframes to ensure their conformity to your product vision.
Prototyping
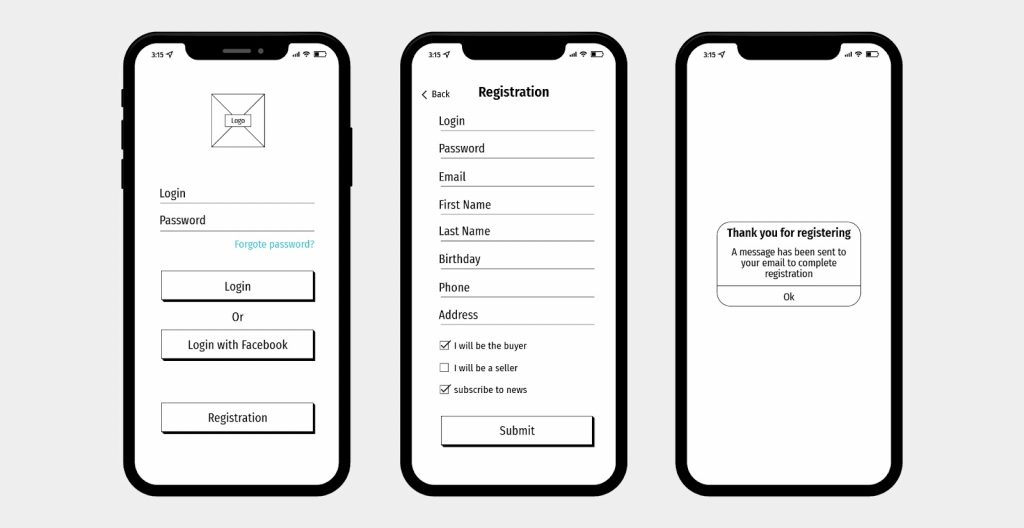
Prototypes are early designs used to get feedback and ideas for product improvements. Unlike wireframes that contain only the structure, prototypes are simulations of the final product design, which means they have elements and content.
Creating, improving, and using prototypes to deliver the final designs of digital products is the responsibility of UI/UX designers. As a client, you will work together with them to ensure that the created prototypes are exactly what you want for your product.
Prototypes look a lot like a finished product, but they contain no code.
Product testing
Before digital products are released, they need to be tested. This means having people use the product and give their feedback. Product testing typically generates a lot of feedback, which is analyzed to find worthy ideas for improving the design.
UI/UX designers participate in feedback collection and analysis. Their expertise is needed to identify those improvement opportunities and ideas, and implement them if necessary.
Most common types of product testing include:
- Contextual testing. Users are asked questions as they are using the product, typically in their own environment.
- Session recording. Involves recording user interactions with a product and further analysis of the sessions.
- Unmoderated remote usability testing. Done with no moderator, remotely, using participants’ devices.
Development of Style Guides
A style guide is a document that UX designers create to compile all design guidelines for a specific digital product. The guidelines contain color schemes, fonts, icons, and other UI elements used in the product.
Style guides are crucial to developing digital products because they serve as a source of truth for UI guidance for the software development team. A properly made guide means the developers will have an easier time creating a consistent design.
Been thinking about creating a website for your business? Here are 10 Types of Websites to help you find out which one you need. Also, see these 20 Brilliant Website Designs to get some inspiration.
Key Skills of UX/UI Designers
To perform their job well, UI/UX designers need to have a broad set of both technical and soft skills. Below, I described how each important skill helps them to deliver high-quality digital products.
Technical skills:
- UX research techniques to discover the needs of users
- UX analytics to analyze user activity on the digital product
- Information architecture to ensure logical product structure
- Product usability testing to discover issues and improvements
- Development of style guides to help keep product design consistent
- UI Prototyping & wireframing + tools to create visualizations of the future product
Soft skills:
- Empathy to understand the needs of target users
- Curiosity to find the best ways to design products
- Flexibility to handle on-the-fly requests and improvements
- Communication to convey their ideas to other team members
- Openness to constructive criticism to adopt design improvements
Outsourcing UI and UX design is a proven business strategy to reduce costs up to 60% and get access to a wider pool of talent.
Check out these guides to learn more:
- 10 Examples of Outsourcing
- Pros and Cons of Outsourcing Software Development
- Offshore Software Development: Everything You Need to Know
How to Work with UX/UI Designers (For Business Owners)
Are you someone who’s planning to develop software to grow their business? If yes, then you’ll be working with UI/UX designers many times throughout your software development project.
Thee tips to collaborate with UX/UI designers should be helpful:
- Meet with them regularly. Workshops, video meetings, and interviews encourage information and feedback flow, which is needed for idea exchange and constant improvement.
- Share information about your target users. If possible, provide info such as consumer research to help designers understand the needs of the target users as well as create user personas.
- Be open, detailed, and honest with your feedback. This improves communication and collaboration as well as contributes to finding better ways to create customer-centric products.
Find UI/UX Designers for Your Project
Have a product idea in mind?
Looking for experienced designers?
Consider outsourcing UI/UX design to a reliable, highly-rated software development company: IDAP Group. We have a 4.9-star rating on Clutch and helped 200+ businesses build high-quality digital products.