Stable and steady.
That’s the best way to describe the progress of AI in agriculture.
The industry, despite being the least digitized, has finally seen momentum for the development and application of various AI technologies.
Finally, more farmers and companies see the value of AI-assisted processes. Healthier crops, real-time field condition monitoring, higher process efficiency, reduced need for manual labor, and better harvest quality—those are just some of the benefits.
In this post, we’re looking at the state of AI in agriculture to give business leaders insights into the current and emerging trends in the industry.
You’ll learn:
- What is AI in agriculture
- Benefits of using AI in agriculture
- Challenges in adopting AI agriculture software solutions
Agriculture software development? That’s us. Get a free consultation from a full-cycle software development company.
What is AI in Agriculture?
AI in agriculture, also known as precision agriculture, is the application of artificial intelligence (AI) solutions in the agricultural industry. The technology is used for field harvesting, health monitoring, weed and pest control, detection of nutrient deficiencies in soil, and other tasks.
Business interest in exploring and developing AI solutions for agricultural applications is reflected in the latest market figures. The overall AI in the agriculture market is projected to grow from $1 billion in 2020 to $4 billion in 2026. This graph has more details.

Benefits of Using AI in Agriculture
As we’ve just seen in the image, agricultural businesses employ such AI solutions as machine learning, predictive analytics, and computer vision. But how do they translate into specific and appreciable benefits?
We’ve examined the latest evidence (scholar studies, success stories, and our company experience) and selected these benefits:
- Automatic weeding
- Automatic harvesting
- Plant disease detection
- Improved soil health monitoring
- More efficient irrigation of farmland
- Application of pesticides and herbicides
Automatic weeding
Weeds steal sunlight, nutrients, and make it easier for pests to harm crops. Today, farmers have one more weapon against them, the kind that replaces manual labor:
A robot that uses lasers to kill 100,000 weeds per hour.
Think that’s science fiction? Not at all. Already, there are multiple models of autonomous weeders available, including from well-known agricultural startups Carbon Robotics and Farmwise.
Here’s how a robot removes weeds:
- Robot drives through crop fields
- Cameras underneath show crops and weeds
- AI software identifies weeds and gives a command to remove them
- High-energy lasers eradicate weeds using thermal energy, without disrupting the soil
Here’s a view of the planted row of crops from the robot’s camera. As you can see, AI software assigned each crop type a unique ID. It’s a way to differentiate them from weeds that have no IDs.
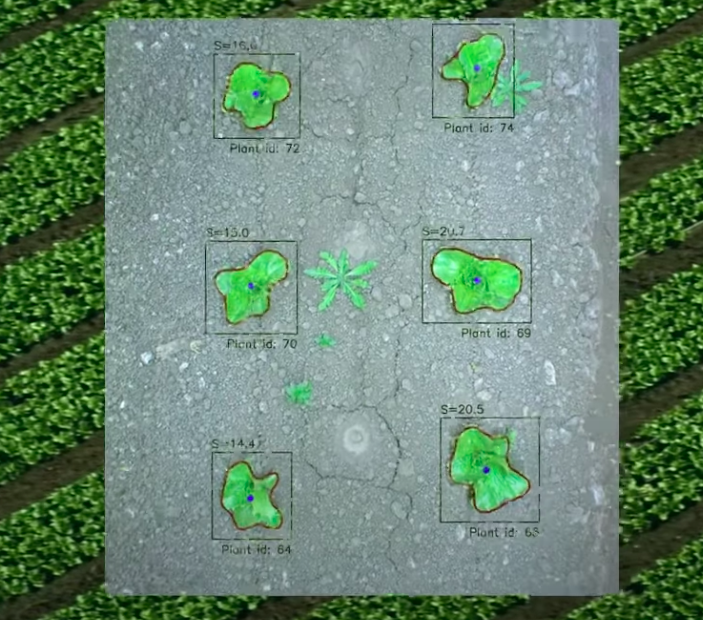

And a great thing is…
You can control this process on your smartphone. All that’s needed is a custom mobile app developed for this purpose. Yeap, so you can dispatch your robotic laborer in the morning and watch its progress from anywhere.
If you have more questions about how autonomous feeders work, this process was also nicely illustrated by Trend Hunter. Take a look.
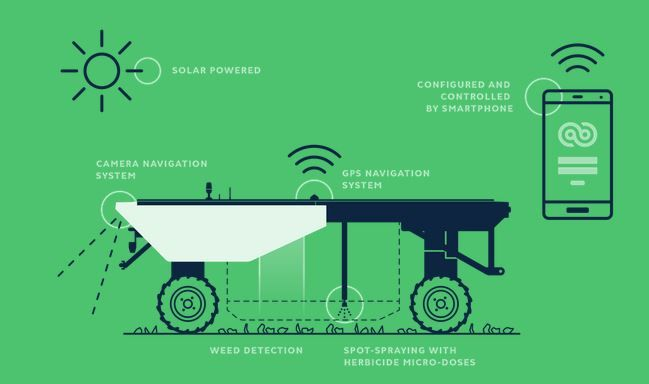
Various manufacturers suggest different performances of weeding robots.
Here are some highlights based on our findings:
- Processing speed: up to 12 acres in 9 hours
- Fully autonomous thanks to camera navigation
- Precision guidance (GPS and camera)
The gains for using automatic weeding robots are huge. In addition to reducing the need for tedious manual labor, they also minimize the use of herbicides, which helps with keeping soil healthier and producing higher outputs.
Automatic harvesting
Costly.
Tedious.
Dangerous due to the higher risk of spreading COVID-19.
Those are the words associated with the manual harvesting of many products. Due to inefficiency and slow speed, agricultural businesses are losing money because of a lack of automation. That’s why we now have automatic harvesting systems entering the market.
An automatic harvesting robot has:
- Camera
- AI software
- Mechanical arms
The software uses the camera to recognize vegetables or fruits and instruct the arms to pick them up. Although it may sound like such a system is slow, reports suggest that a robot is more efficient than humans, works 24/7, and is over 90% effective.
So far, robots for collecting peppers, lettuce, tomatoes, strawberries, apples, and other fruit and vegetables. Sweeper, the autonomous robot you’ll meet in the video below, for example, can even recognize when peppers are ripe and ready for harvesting.
The beating heart beyond this innovation: predictive analytics.
It’s a set of AI and machine learning-powered algorithms that uses historical data to predict future events. Simply put, AI engineers “train” the algorithm to detect objects (fruit and vegetables, in this case) so it works autonomously.
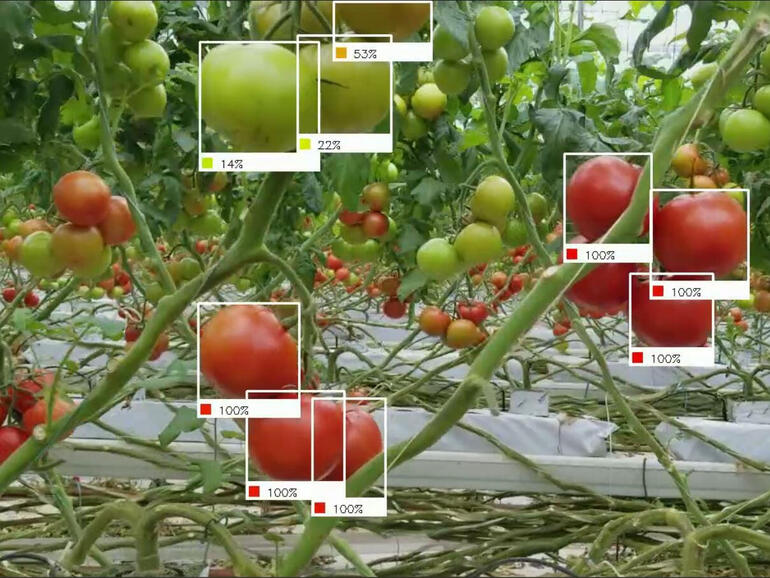
An automatic harvesting robot’s camera would see something like this while working. Each detected reachable object would have been recognized, perhaps even with percentages indicating ripeness.

Have you heard of agricultural Customer Relationship Management systems (CRM)?
They help to:
- Keep all customer information in one place
- Control of finances and documentation easier
- Have quick access to Inventory of equipment and products via computer
Many growing agricultural businesses have adopted CRMs to improve overall efficiency and automate business processes like customer base management and accounting.
Read more about CRMs:
- What is a CRM and How to Choose One
- CRM Types and Their Business Functions
- How CRM Helps improve customer service
Plant disease detection
Between 20% to 40% of global food production is lost due to plant diseases and pests.
That’s why we’ve seen many plant disease identification apps popping up all over the place. They use AI algorithms to detect health problems, and help businesses find and treat crops damaged by pathogens and pests.
The way this intelligent farming solution helps is simple:
- Take a photo of a plant
- App will run the photo through image recognition software
- Software generates disease information, treatment recommendations, and/or identifies a pest plant
Plantix is one of the apps proving how useful this AI agriculture innovation can be. The developers behind the app have created a database of 100,000 photos of sick plants, which is used by AI-powered image recognition to identify over 60 diseases.
For example, Plantix recognizes powdery mildew, a common fungus that affects tomatoes, peppers, melons, squash, and lettuce, within seconds. Here’s a 2-minute video explaining how the app works.
What drives this AI agriculture innovation?
Machine learning analysis.
AI-powered image recognition software compares input photos against its database of images of sick plants to generate results. The machine learning algorithm looks for characteristic patterns of plant diseases (mosaic-like discoloration, spots, etc.) to identify the problem.
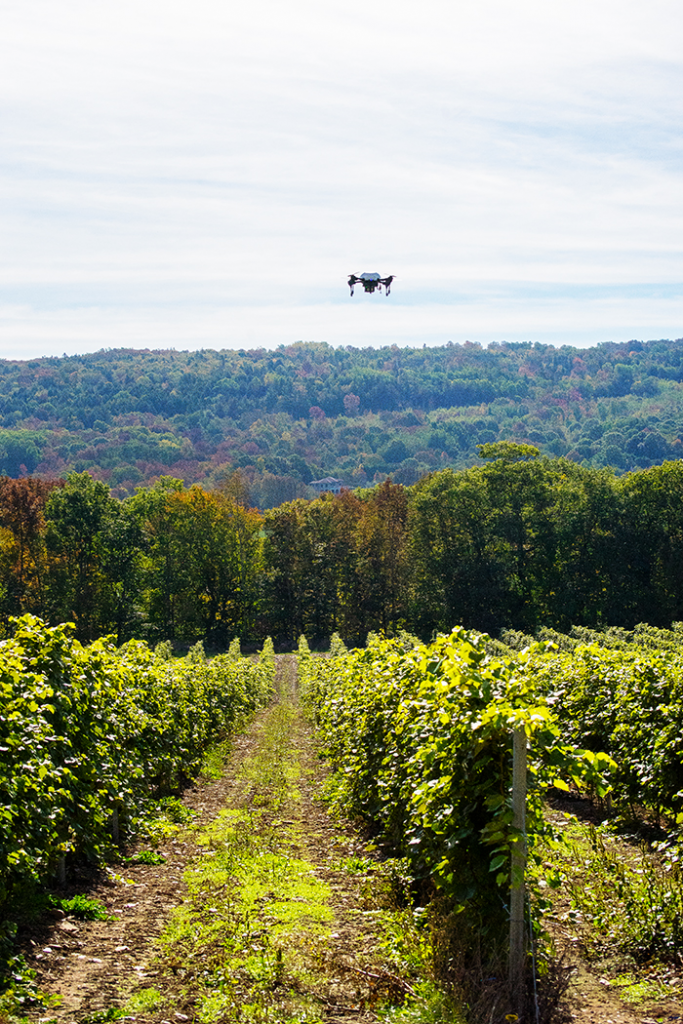
Disease-detecting AI software can also be installed on cameras inside greenhouses, on drones, and other agricultural equipment. This way, farmers can recognize crop illnesses faster and respond with preventive measures.
Already, Drones with AI software are monitoring the health of fields such as vineyards all over the world. In this case, the technology helped reduce losses from the disease of wine grapes by up to $15,000 per acre.

Machine Learning (ML) is an essential part of AI that basically means “learning from data.” If you’d like to learn more, our guide on Types of Machine Learning will help.
Improved soil health monitoring
The ability to detect disease in the soil is extremely important to prevent yield loss. Most farmers rely on traditional soil analysis techniques, but their results aren’t always enough to prevent diseases and other issues.
That’s where AI has already started making a difference.
Soil analysis with AI works like this:
- Soil sample is taken to identify all present microbes and content
- Machine learning algorithm compares the data from sample against a huge database of soil data
- Results indicate the moisture level, nutritional deficiencies, pH level, microbes present in the sample, and other factors
- Specialists process the results and define risks of specific diseases as well as give treatment recommendations based on the soil content and microbes
Unlike traditional methods, this agricultural AI innovation offers more comprehensive and accurate soil biology and chemistry analysis. That’s why farmers who use machine learning for soil analysis say they get more useful info about pathogens, which helps them inform their strategies instead of guessing what’s in the soil.
Matthew and Joe Schweigert, the owners of Schweigert family farms, are an example. According to them, the conventional soil analysis is “nowhere near” as deep as the AI-driven, so the guesswork was eliminated from their work.
Here’s Schweigerts’ interview about their collaboration with an AI startup that developed the test, Trace Genomics.
More efficient irrigation of farmland
Agriculture irrigation accounts for 70% of water use worldwide. With crops requiring huge amounts of water, farmers are looking for ways to eliminate inefficiencies and achieve the optimal use of the resource.
Agriculture AI can help. Already, there are drones equipped with AI software that use advanced analytics and make high-resolution aerial imaging to collect information about irrigation systems on fields. Constant monitoring reveals problems like clogs and leaks as well as evaluates soil health.
Here’s how this AI agriculture system works:
- AI software is integrated with drones
- Drones are flown on a weekly basis over fields
- Cameras onboard drones take aerial images of fields
- AI software analyzes the footage and reveals irrigation system problems and areas that might need more water or fertilizer
- Farmers access the analysis on their computers and make decisions to prevent problems (often weeks before they become apparent)
Aerial footage analyzed by AI looks like this.
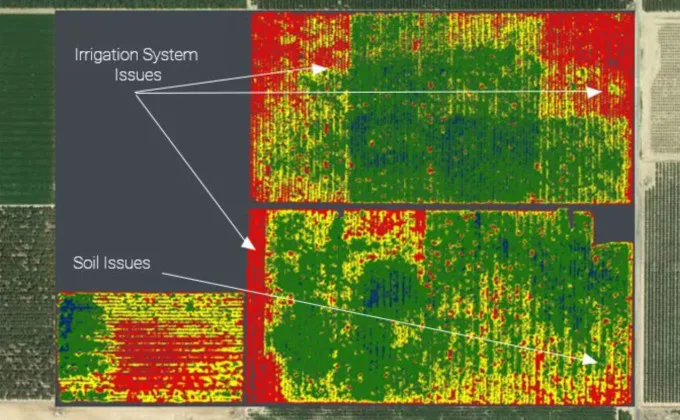
Using this AI agriculture technology, farmers can use less water and, consequently, fewer chemicals, to keep fields healthy. In the long run, they can grow higher yields, save money, and improve the quality of products.
Application of pesticides and herbicides
AI and machine learning in agriculture can also define when plants are injured or sick. Once again, this technology analyzes aerial images of fields and determines where to spray pesticides and herbicides.
For example—
The images below were taken by drones. They show two different problems detected by AI-enabled image recognition software: pest damage and plant wilting.

By analyzing thousands of images taken by drones on a consistent basis, AI helps to detect problems even on small scales.
Benefits of such AI analysis:
- Identify pest attacks and plant health problems
- Save the excess use of pesticide and herbicide
- Improve soil fertility maintenance
Besides health monitoring, autonomous drones can spray pesticides and herbicides in carefully assigned field areas. Research confirms that crop-spraying drones are effective to simplify field management, reduce human effort, and improve yields.
Crop spraying drones are illustrated below along with other related models used in intelligent farming processes.

As an agricultural business, you can have programmers develop custom AI algorithms to be used in your fields. Feel free to contact us about AI and ML software development you need—we will guide you through everything.
Challenges in Adopting AI Agriculture Solutions
”AI is still too complicated.”
“It’s too soon and risky for my business.”
“Should I make a move now or wait to see more benefits from AI?”
That’s how many decision makers think about adopting AI in their agricultural businesses. Well, as with any other innovation, it’s completely normal to be cautious. But writing AI off as “too complex,” “too expensive,” or “unworthy” is not a good idea.
The reason is simple:
AI in agriculture is NEITHER too complex or too expensive.
As you’ve seen examples and success stories earlier in this article, both farmers and large agricultural corporations are benefitting from AI. So, it’s worth the investment, too.
Besides, all challenges in adopting AI in agriculture are solvable:
- Confusion. Happens when an AI software provider fails to clearly explain implementation and maintenance
- Lack of experience. Continuous education and training are required to help farmers implement AI software and hardware properly
- Outdated digital infrastructure. In many cases, even the latest AI solutions can be incorporated into existing infrastructure (farm management software, tractors, spreaders, etc.)
Summary
AI for agriculture addresses the three most critical issues of farming: overuse of chemicals, tedious manual labor, and process efficiency. The technology is making quick progress, so many agricultural businesses are expected to operate AI solutions within the next few years.
With IDAP, you can build custom AI software to grow your agricultural business.
Our company:
- Has a 4.9-star rating on Clutch
- Is rated in the top 1000 software development service providers
- Has experience building software solutions for agriculture businesses
If you’d like to find a reliable software partner to help you improve your agricultural business, get in touch with us or view our portfolio.



 (5 votes, average: 4.20 out of 5)
(5 votes, average: 4.20 out of 5)