Smart farming is applying information technology for managing farms.
This approach gives farmers tools and strategies to improve yields and sustainability of agricultural production. The heart of the innovation: smart agricultural technology, which is making its way from other industries.
In this post:
Software development for agriculture? That’s us. Hire a reliable technology partner to develop software for your needs.
What is Smart Farming?
Smart farming refers to the use of information and data management technology and devices in agriculture, including software, sensors, and robotics, to increase productivity and efficiency of agricultural systems.
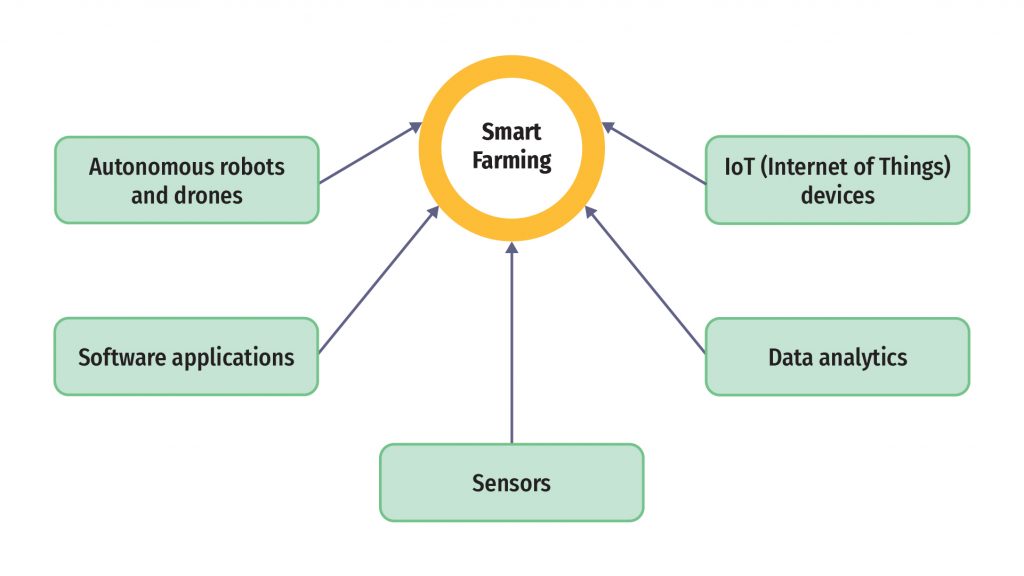
Smart farming promotes the usage of these devices:
- Sensors
- IoT devices
- Data analytics
- Autonomous robots and drones
- Software applications
Why is Smart Farming Important?
About 25% of US farmers (250,000+ farms) are using smart farming technologies at the moment. That’s not a lot, but smart agriculture will become more important than ever before in just several decades.
We need smart farming to:
- Improve crop health. Optical smart farming technologies allow farmers to identify crop diseases and other problems earlier.
- Reduce the ecological footprint of farming. Precision agriculture systems can reduce the use of harmful chemicals and carbon emissions.
- Help feed the increasing global population. The UN data suggests that the world’s population will grow from 7.7 billion in 2020 to 9.7 billion in 2050.
- Provide food security in climate change scenarios. More efficient smart farming helps to adapt to changing climates while maintaining production levels.
- Achieve higher yields while reducing operating costs. Smart farms achieve higher yields (by 1.75%), lower water use (by 8%), and lower energy costs ($17 to $23 per hectare).
So, the greater use of various types of smart agriculture is crucial not only to improve financial performance. It’s also needed to meet the needs of the growing population.
From better finance management to farm management systems, software is one of the most helpful smart farming technologies.
Get in touch with us if you’d like to get a free consultation on how agricultural solutions can help you or if you have a project in mind.
Types of Smart Farming
Farmers have already begun using various smart farming technologies, and their experience has been extraordinary. But these top types of smart farming stand out for their results:
- Farm management software
- Grain elevator management software
- Agricultural robotics
- Livestock management and monitoring
- Smart crop management
- Greenhouse monitoring systems
- Autonomous ground vehicles
1. Farm Management Software
Smart farming software is designed to help with various aspects of farm management. Basically, it’s a hub with historical and real-time data and information about the facility, which farmers use to plan, monitor, and analyze activities.
The software might contain:
- Weather records
- Animal monitoring data
- Farming equipment condition status
- Ideal and historical planting schedule
- Real-time environmental conditions for field monitoring
- Record management (revenues, orders, expenditures, etc.)
- Predictive analytics (yield size, expected waste, profitability, etc.)
Together, this information allows farmers to manage everything using one app. Besides farm management, they can also manage finances and human resources.
Often, this smart farming tool is built as a custom software solution for specific farms to include only the most useful options.
Thinking of designing an end-to-end management system for your agricultural business?We helped 200+ businesses and created business management systems and can consult you and help to create a custom solution.
2. Grain facility management software
Grain facility management software is a system of software (computer programs) and hardware (sensors, trackers, cameras, etc.) designed to assist with proper management of grain, feed, and seed handling facilities (grain elevators, rice mills, etc.)
Grain facility management software can help farmers with:
- Accounting (invoices, tickets, contrats, and other financial data)
- Operational data (inventory, records of procurement, storage, processing of grain, seed or other products) in one place
- Facility maintenance and monitoring in real-time (temperature, moisture, CO2 levels, grain movements, humidity control, etc.)
- Fleet management (sensors for trucks, forklifts, and other moving equipment for real-time monitoring and safety control)
Having this kind of smart farming software allows agricultural businesses to protect grain and seeds, streamline operations, improve safety, and make better decisions, faster.
3. Agricultural robotics
An agricultural robot is a robotic device designed to improve agricultural processes by performing time-consuming or labor-intensive tasks typically performed by farmers, including crop monitoring, irrigation, and data acquisition.
Types of robots used in smart farming include:
- Drones: Used for aerial monitoring of fields, crop spraying, and data collection
- Automated tractors: designed for planting, harvesting, and cultivation
- Mixing and feedings robots: made to compile food ratios and deliver them to designated herds
- Robotic Harvesters: Specialized for picking fruits and vegetables using robotic arms, without damaging the plants
- Soil analysis robots: they conduct soil sampling, nutrient analysis, and pH measurement on a predefined schedule or in real-time
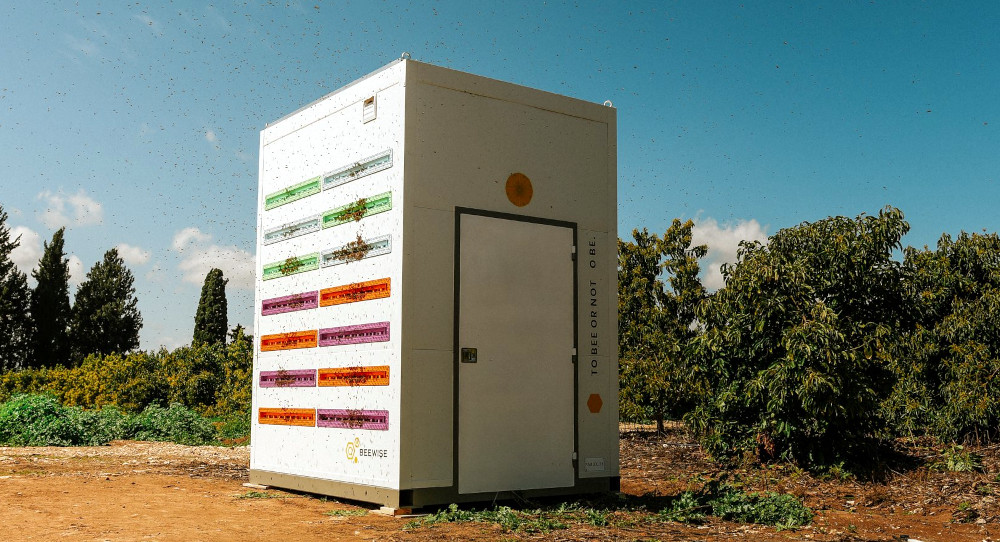
- Beekeeping robots: Designed for temperature monitoring, honey extraction, and water and medicine dispensing (see an example below)

4. Livestock Management and Monitoring
Also called Precision Livestock Farming (PLF), this technology uses IoT devices and predictive analytics software to track aspects of livestock.
These aspects include:
- Behavior
- Feeding patterns
- Health and well-being
How exactly does PLF work?
Let me share an example—
Suppose we manage a large farm with hundreds of cows. We’d like to monitor their health, optimize feeding patterns, and conduct real-time monitoring. The smart farming equipment for this project would have cameras, sensors, and an app.
This equipment can identify:
- Lameness
- Aggression
- Abnormal postures
- Prolonged inactivity
- Unusually shorter feeding sessions
- Shorter step frequency and step length
- Changes in tail positions (signs of tail biting)
These aspects can be signs of disease, well-being risks, and aggressive behavior. The software can give farmers real-time health status even for individual animals, from as small as chickens to as large as cows.
For example—
By analyzing the motion curve generated by the leg swing of an individual cow (as shown below), an automatic smart farming software gives alerts about lameness.
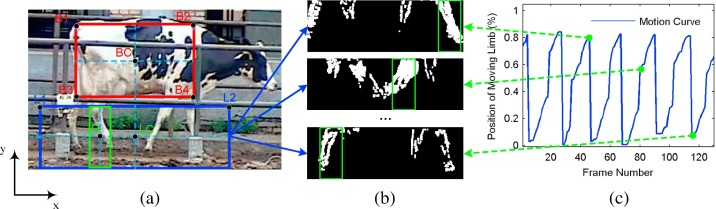
AI-enabled computer recognition is the smart farming technology that makes livestock management and monitoring possible. Farmers can even recognize facial expressions in sheep, giving an early warning of diseases such as mastitis and foot rot.
All these technologies give farmers a real-time monitoring ability, which is critical in the industry, where health status has a major economic impact.
5. Smart Crop Management
Traditionally, farmers have gone to the fields to check on the health of their crops. But imagine you have to inspect your field for hours every day—for large agricultural businesses, this method is simply impractical.
Enter smart farming.
IoT sensors and drones have proven the most valuable for farmers. So, let’s take a closer look at their contribution to crop management.
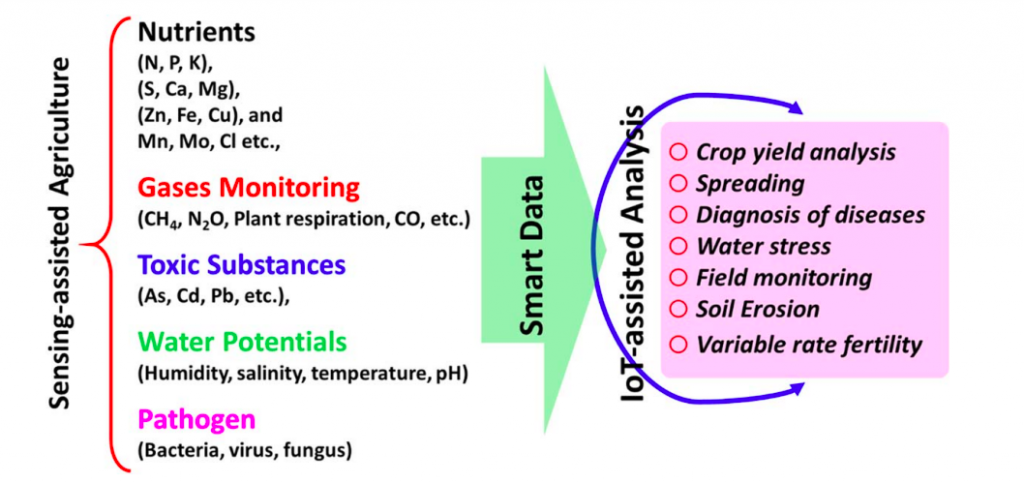
First, sensors.
Installed on fields, these devices can provide on:
- Moisture levels
- Pesticide levels
- Ambient temperature levels
- Soil properties (organic matter, clay, etc.)
- Presence of CO2, O2, and other gasses + pH levels
Sensors come in different types (weather stations, optical, electrochemical, etc.) and can provide both real-time and historical data on crop health.
The Electrochemical Society beautifully visualized the whole range of data that smart farming sensors provide, along with the benefits.
The second device category, drones.
Farm drones can:
- Inspect soil health
- Assess irrigation needs
- Define crop health and maturity
- Detect crop damage caused by pests
- Conduct aerial treatment for crop diseases, weeds, and pests
The technology that makes these operations possible is AI-powered software. Agricultural applications use GPS, image recognition, and various IoT devices to guide drones and let them perform their functions.
Here’s an agricultural drone with an onboard camera equipped with AI software (image: Shutterstock).

So, how exactly can this smart farming technology help?
Let’s consider two use cases: pest detection and spraying.
A sensing drone found unusual forms of plant leaves, suggesting potential pest damage. The image recognition technology ran comparisons with preloaded pictures of healthy leaves and detected abnormalities.
Farmers review the evidence and deploy an actuation drone to distribute the pesticide. The device has an onboard fertilizer tank, so it can spray the affected area with great precision.
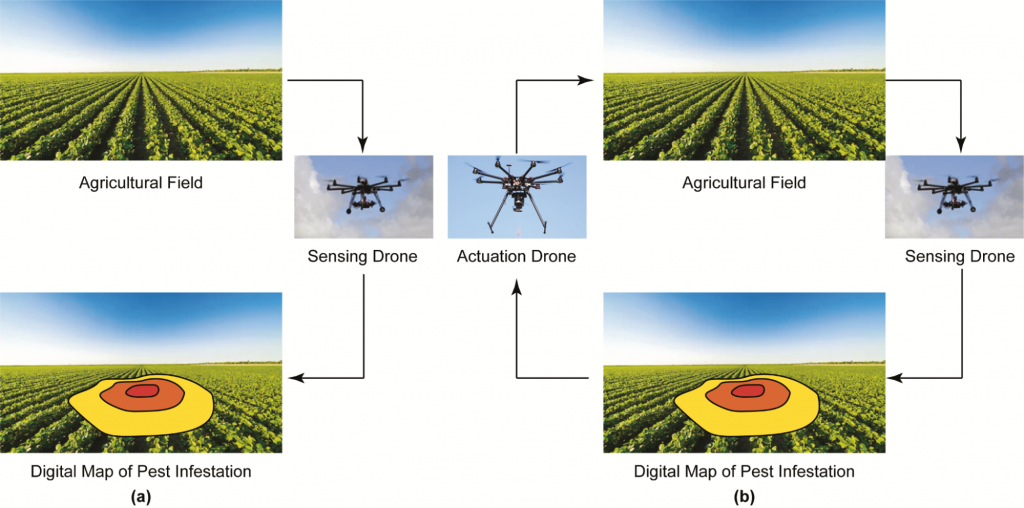
This way, farmers can detect potential problems earlier and prevent them. By monitoring fields continuously, they can maximize yields and minimize losses.
Want to learn more about AI and drones in agriculture?
We have another great post for you: AI in Agriculture: Examples, Benefits, Challenges [Latest Data]
6. Greenhouse Monitoring System
A greenhouse monitoring system, aka “smart greenhouse,” is a greenhouse equipped with sensors controlling environmental conditions automatically.
The essential components of the system include:
- Sensors
- Wireless connectivity (infrastructure + cloud)
- User software (a desktop and/or a mobile app)
Here’s how these three components combine to generate data on conditions.
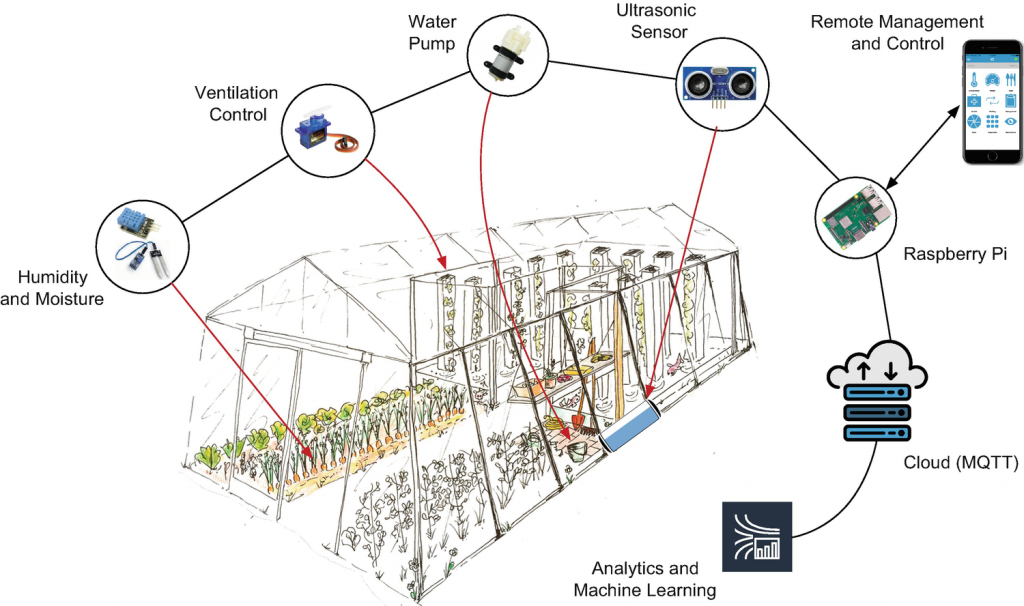
Thanks to this system, a smart greenhouse:
- Maintains an ideal micro climate. Temperature, humidity, light, and other IoT sensors control environmental conditions.
- Manages fertilization and irrigation. Sensors collecting soil health data provide data based on which farmers can activate sprinkler and irrigation systems.
- Provides data on potential plant diseases. Continuous environmental readings can help farmers recognize diseases and pest damage and take action early.
This smart farming technology removes the need for farmers to control environmental conditions manually. The data received by the software can be easily viewed and analyzed, providing unprecedented insights into the health of plants.
More agricultural businesses start using this smart farming technology to generate higher yields while reducing overall operating costs.
Manufacturing is another major field where IoT is actively used to increase the productivity and efficiency of operations.
Learn more: Five Uses of IoT Apps in Manufacturing
7. Autonomous Ground Vehicles
Drones aren’t the only robots involved in smart farming. Autonomous driving technology has also arrived in tractors and other agricultural machinery. It’s made autonomous farming possible and reduced the need for human labor.
The technology itself is fairly simple—
AI and location tracking software containing map data programs the vehicle’s position and controls speed. So, it’s just about GPS and controlling equipment counted on the machinery (cameras and sensors)
Simple as that.
That’s why self-driving tractors in particular are becoming a norm—the U.S. alone has over 10,000 unique and retrofitted units. Here’s how one of them looks like.

Here’s what autonomous vehicles mean for farms:
- Elimination of human errors
- Increased fieldwork accuracy
- Reduced need for human labor
- Optimized production schedules
- Doing repetitive work (digging, spraying, harvesting)
The ultimate goal of this smart farming technology: enable super precise farming while alleviating farmers from having to be involved in field activities.
AI is everywhere in smart farming. But the technology is also helping businesses in many other industries.
Here are some reads if you’re interested:
Summary
Smart farming technologies become more and more important with each day. Agricultural businesses of all sizes are already using software and IoT devices to increase food production and get a competitive advantage.
But the market for smart farming is still developing, so there’s a good opportunity for businesses to become early adopters. Creating custom intelligent farm solutions within the next five years should give them a competitive advantage.
If you’d like to know how your agricultural business can improve operations with smart farming software, feel free to contact us. We’d be glad to share our expertise and help you find opportunities to advance your business.




 (3 votes, average: 3.67 out of 5)
(3 votes, average: 3.67 out of 5)