MVP development begins with analysis. When you approach the development, it is assumed that you already have an idea and “intuitive understanding” of what your users need and what they are willing to pay for in the future. It is time to study these ideas carefully. Why should I create MVP and what are the goals of this process? Creating an MVP answers the following questions:
- What problem or task does the product solve? What’s new in what you do?
- Who will use this product and who are your end users?
- How do you solve the problem now? What competitors, similar products and alternatives are already on the market?
- What is your market and what is its potential volume? How fast does it grow? Who is the “biggest and worst” in this market?
- What is your business model? How fast do you grow? What encourages users to talk about you? Why do users switch to your product?
- How does your team work? What experiences? What is your personal motivation for this product? What outcome do you want to achieve?
What Does the Abbreviation MVP Mean and What are the Goals When Creating it?
The concept of MVP (Minimum Viable Product) is a demo version of a program or website with just a basic functionality that allows you to understand whether you want to implement a specific function, what exactly your users need, and so on.
The main task of the MVP is to reduce financial costs. You need to convince the user of the effectiveness of the product in advance in order to better sell it.
This is necessary for developers. However, keep in mind that MVPs should be of high quality and should not be created in a hurry. Otherwise, you will lose the trust of users and will not be able to fully successfully show all the power of the functionality of the created product.
The Ultimate Purpose of Creating an MVP?
We can say that MVP tests working hypotheses and allows you to implement new necessary ideas for success in the product among potential users. You must first create an MVP to make sure your product can become popular.
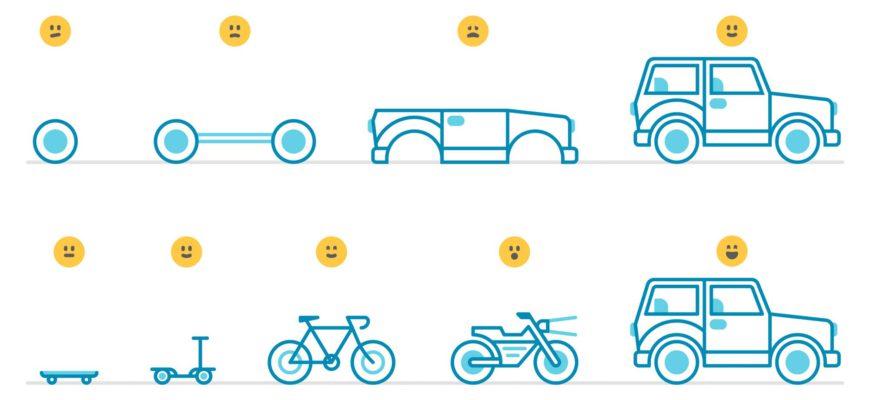
From the above, we can draw simple conclusions about the goals of a minimum viable product:
- Carefully test your hypothesis on real data to determine the reality of your idea;
- Entering the market;
- Collection of the first base of potential customers of the product;
- Reduce the financial costs of development by removing unnecessary features from the product.
Of course, if it turns out that after the launch of the MVP of the product, no one is interested, you can avoid financial losses.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Creating an MVP
It is difficult to write a step-by-step procedure for creating an MVP product, as it largely depends on the project itself and current market conditions.
Step 1. Define your goals
If there is no ultimate goal, there is no fully functioning product. You need to quickly determine why a potential customer needs your product and why they should buy it. After answering these questions, the tasks to be solved with the help of MVP become clear.

Step 2. Carefully analyze your target audience
Many people make the common mistake of creating an MVP for several categories of different people at once. Finding good objective reviews about a product in such a case can be difficult due to a large number of non-target audiences, non-target users of your end product. The ideal option is to narrow down your target audience.
Think about who your ideal customer is. It is important to clarify as many details as possible:
- Age;
- Income;
- Level of interest in the product;
- Place of residence, etc.
You need to test your product to get true feedback from your ideal customer, your target audience.
Step 3. Learn about competitors
No one says your idea is unique, but we strongly encourage you to explore the competition for your product. Such a program or product may already be somewhere. In this case, your task is to clarify the following points:
- What competitors offer;
- The marketing tool they use;
- What market share they occupy.
This allows you to customize your solutions for the product to enter the market.
Step 4. Write a clear description of all available features
The product can solve many problems at once, but you do not have to talk about everything during the trial period. At this stage, you need to highlight the most important functional features. Just give a few options. They should be the basis for the MVP. All other features will be added after the product is fully launched.
Step 5. Perform a SWOT analysis
This analysis identifies the strengths and weaknesses of the product. It is important to understand the vectors of threats, risks, opportunities, and change. All this must be taken into account when developing an MVP. You shouldn’t think of a demo version of a project as a few hours spent. So it doesn’t work.
Your main task is to focus on the strengths, minimizing the risks of threats and weaknesses of the project.
Step 6. Choose a specific development methodology
There are several ways to develop an MVP. Choose the one that best suits your project and get started:
- Lean is a quick response to feedback. MVP is created, and tested, user feedback is collected, changes are made, etc. This process continues until the final project is launched;
- Scrum. This method is somewhat similar to the previous one but divided into cycles. In short, the project launch cycle, the feedback cycle, the product update cycle, and so on;
- Boar. Here the problem is solved when it appears. This method works great after the release of the first version of Minimum Viable Product;
- XP. This option is only suitable for software. The program code is written. The attention to design and functional details is not paid by developers. The program must work properly.
Step 7. Test product feasibility
Regular testing is required when creating an MVP. There are two types of product testing:
- Alpha testing. Internal analysis of the program. It is made by developers and product owners. The goal is to evaluate the product, identify problems (if any) and solve them;
- Beta testing. Testing is performed directly by real users. They are given access to the program for 1-2 weeks. Users take full advantage of this software product and leave their comments on the operation, which can be added, improved, or changed to developers.
Main Mistakes When Creating an MVP
The main mistake when creating such a test product is a careless approach to creating an MVP. Some people think if this is a demo version, why worry? It is important to take MVP as seriously as possible.
Consider the most common mistakes when creating an MVP:
- The desire to be perfect. You don’t have to see everything in your head at once. It is important to focus on the main features to show users the benefits of this product;
- Ignore comments. The purpose of MVP is to get user feedback. It is important to listen to their opinions, draw conclusions, and correct mistakes;
- Publication. Many development companies are announcing great functionality and many new features in their product, emphasizing their uniqueness and exclusivity. Don’t exceed customer expectations, as MVPs may not work.
Summary
IDAP is a good team to create MVP, thanks to its experience, skills and business practice in developing its own products. If at the stage of MVP creation, you can create a really functional product, you can save a lot of money and years of optimization.
It is very important that the MVP phase really ends. Statistics show that many startups will fail because the development team cannot run the minimum version. In the case of IDAP, this risk does not exist. They start the project on time and within the framework of the defined budget.
If MVP is successful, they know that the problem/solution is correct. To do this you need to do it, check your users and collect positive feedback.