In 2019, The Economist identified the “second phase of the internet”—the Internet of Things (IoT). Together with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data, IoT currently stands at the center of the digitalization of the global economy. Smart devices in combination with mobile applications have enormous market potential. Given the continuous development of wireless networks, sensors, and computing capabilities, the Internet of Things could be the next frontier in the race for dominance in the digital realm.
What is the Internet of Things and what IoT applications are there in different industries? You will find answers to these questions in this article.
What is IoT?
IoT stands for the Internet of Things. It is the fast-growing network of devices (“things”) like smartphones, cars, and manufacturing robots. These “things” have embedded sensors, software, and other pieces of technology that enable them to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems via the Internet.
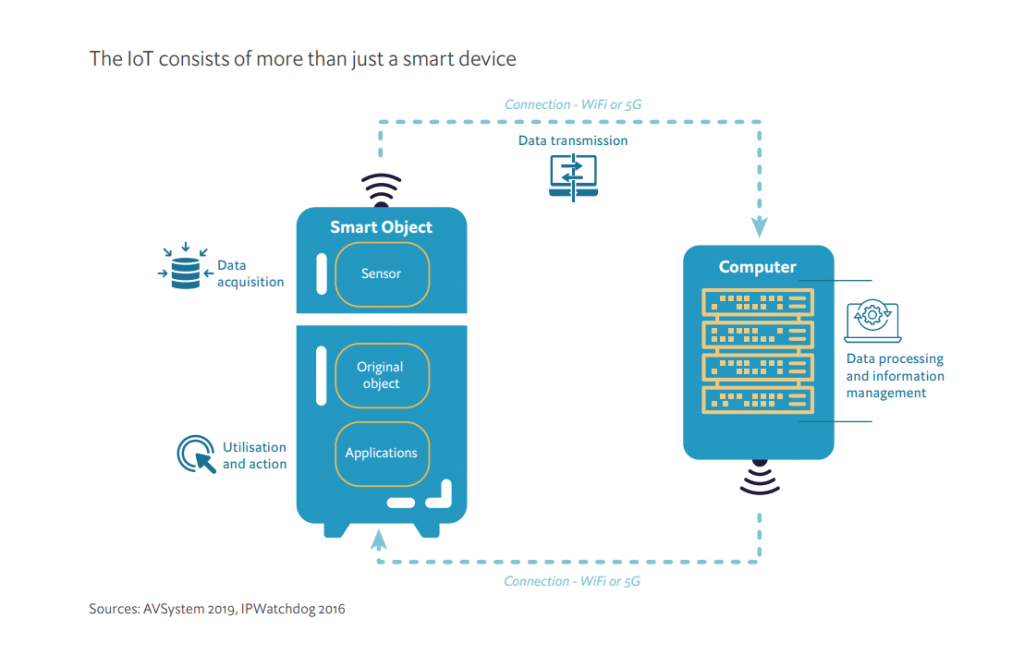
The sheer concept of IoT has two defining features: automation and connectivity. What it means is that there is communication between several individual devices, machines, and other hardware on a global scale (connectivity) without humans being directly involved (automation).
What technologies made IoT possible?
More and more electronic devices are becoming Internet-enabled each year. It was forecast that number of IoT devices would reach 8.74 billion in 2020 alone. It means there are currently more IoT devices than humans on Earth! It also proves how integrated technology is becoming not only between various devices but also in our daily lives. And if that wasn’t enough, the number of “things” continues to increase to nearly triple by 2030.
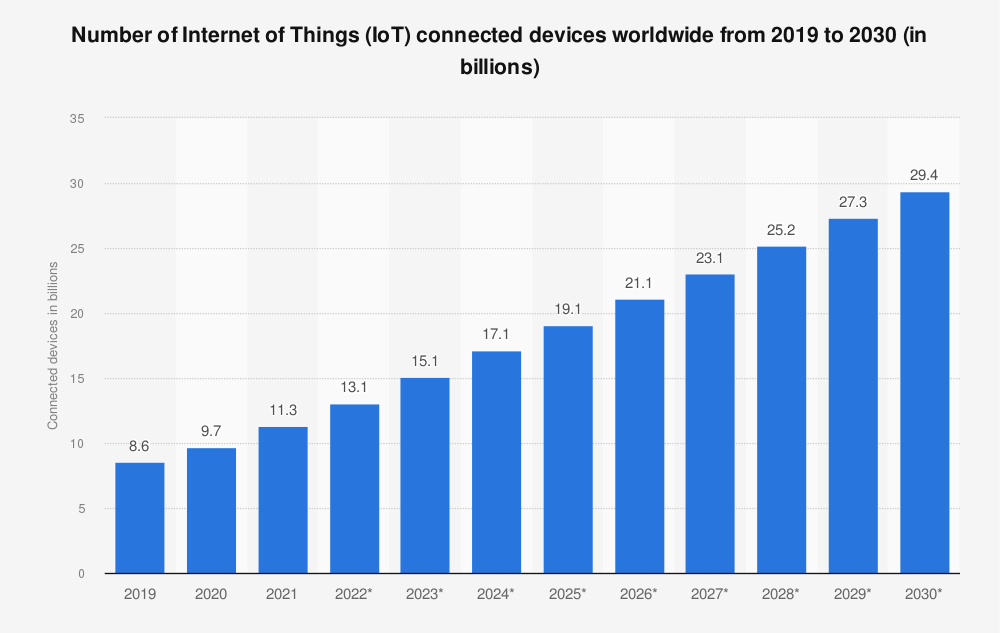
What does this technology owe such a sharp increase in a variety of IoT-connected devices?
Affordable sensors
Technology cannot be popularized and made accessible if potential users cannot afford it. Or, when it requires a high amount of energy. However, today, sensors became not only more reliable but also more affordable and less energy-demanding allowing many devices to become commercially available.
Connectivity
The Internet and connectivity lie at the heart of IoT. Many new network protocols designed for the Internet have made it easy for sensors to connect to the cloud and to other “things” and transfer data between them more efficiently.
Cloud computing platforms
As the availability of cloud platforms has increased, it enabled businesses and consumers to access the infrastructure they need without worrying about managing or maintaining it.
Machine learning and analytics
Machine learning and data analytics (allied technologies), as well as huge amounts of data stored in the cloud, push the boundaries of the IoT. Not only do all of these make IoT possible but also enable the interconnected devices to generate even more data that further feed machine learning which, in turn, makes IoT-enabled devices work much smarter.
Conversational Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Although we still have a long way to go in the field of AI, the recent advances in neural networks have paved the way for Natural Language Processing (NLP) in IoT devices. As a result, digital assistants like Alexa and Siri became affordable and viable technology for home use.
What are the different IoT applications in business?
The Internet of Things has steadily gained momentum and is now boldly shaping our future. The IoT applications have entered many different business industries and bridged the physical world with the digital one. As a result, work and daily activities became much easier. Some of them were even completely automated.
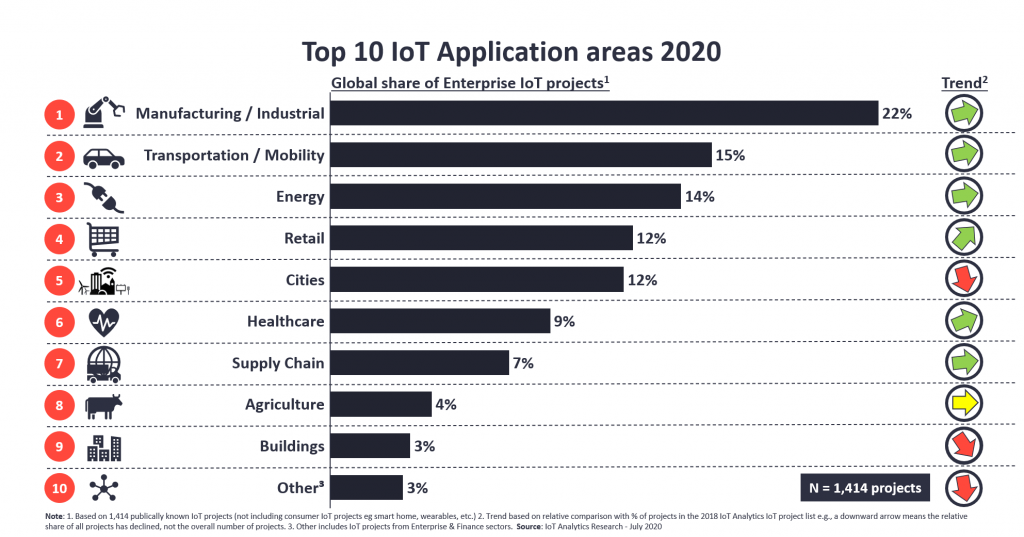
IoT will have a particular impact on sectors that are focused on the making, moving, or selling of physical objects, ranging from drugs to electric vehicles. Let’s take a look at some of the most prominent IoT applications in different industries.
Smart homes
You will find one of the top IoT applications in home settings. Smart homes feature internal systems that enable the control of appliances automatically and remotely via the Internet using a device such as a phone.
Examples of IoT used in smart homes range from intelligent utility systems to entertainment. For instance, IoT applications can track daily electricity and water usage to help smart home dwellers make more informed decisions about their expenditures.
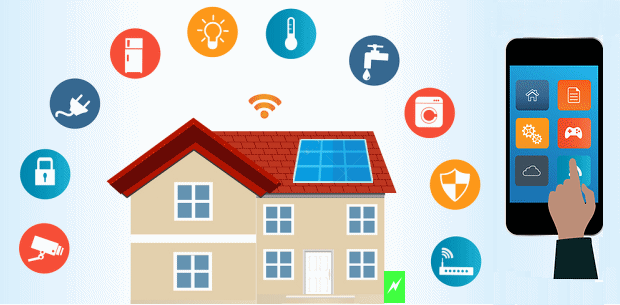
Furthermore, systems like automatic illumination, door locking, a garden irrigation system that responds to current weather conditions, and surveillance also come under the umbrella of IoT applications found in smart homes. The best part is that all those systems are connected and can be operated through the mobile application.
Wearables
Wearable technology is a hallmark of IoT applications. These devices serve a wide range of purposes ranging from medical, and wellness to fitness. You will find IoT applications in fitness bands, heart rate monitors, and smartwatches.
Since those wearable devices are equipped with a variety of sensors and heterogenous wireless protocols, they can also be used to enact a variety of people-based Social Internet of Things (SIoT). Wearable IoT devices also have a bright future in healthcare with the passive and remote monitoring of vital readings like heart rate and blood pressure.
Smart city
Not only do homes and watches get smarter thanks to the IoT—the same can be said about the cities. Smart cities use IoT devices such as connected sensors, lights, and meters to collect and analyze data. Then, the cities can use this data to improve infrastructure, waste management, safety, and services, environmental issues, and more.
Smart grid
One of the greatest implementations of IoT-enabled architecture in smart cities is smart grids which help tremendously with energy conservation.
Considering the global climate crisis and the immediate need for far-reaching innovations in the energy sector, the IoT can be one of the solutions we need. IoT can support changes to power grids at a system level and help end-users conserve energy in their homes.
A smart grid entails two-way communication between the utility and its customers. It consists of controls, computers, automation systems, new technologies, and equipment that work together with the electrical grid to respond digitally to a quickly changing electric demand of citizens.
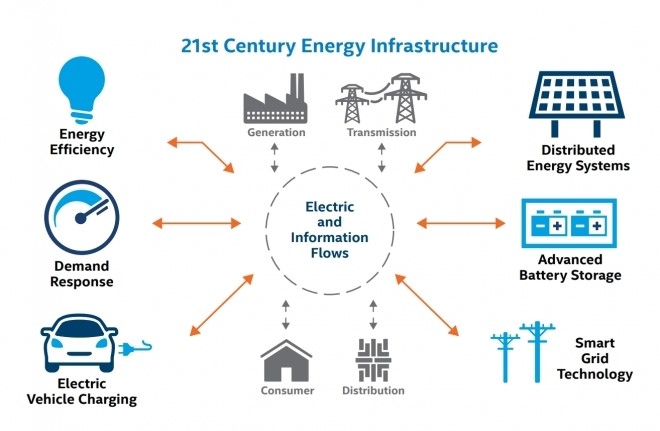
The intelligent power grid “knows” its users and their habits by monitoring the behavior of energy consumers. Thanks to this, it can predict how much energy users are going to need and when.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
Industrial IoT (IIoT) is the subset of IoT technology that specializes in IoT applications in industrial settings. These include farming, manufacturing, oil and gas, and utilities. Although both IoT and IIoT rely on the same technologies (sensors, cloud platforms, connectivity, and analytics), this is where their similarities end.
IoT is mostly about human interaction with objects (the “things”) like cars, digital assistants, thermostats, and so on. IIoT, on the other hand, is used to monitor and control production processes. Simultaneously, it collects data for quality management and documentation. This way, the IIoT technology allows for closer tracking of more parameters and more control over manufacturing processes.
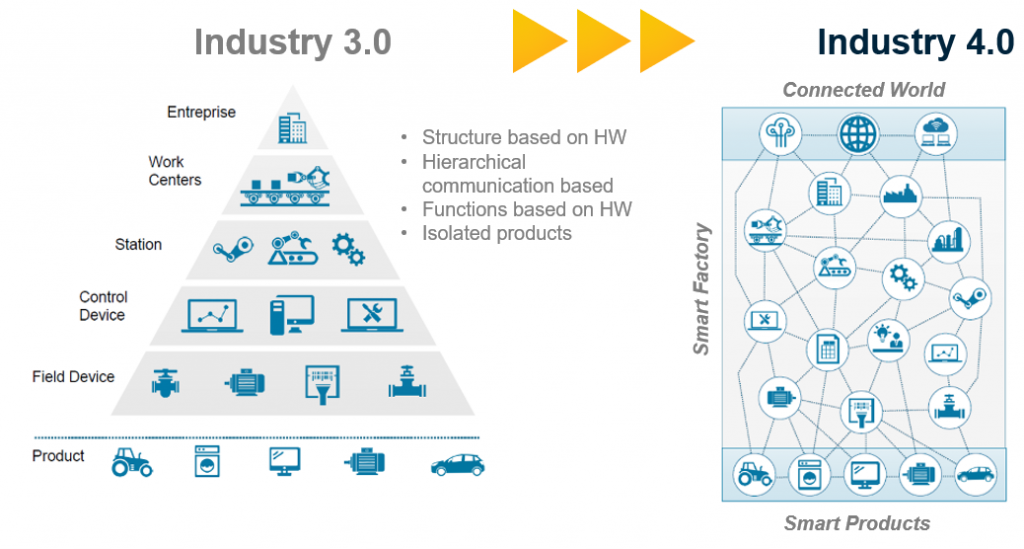
IIoT is sometimes referred to as the fourth wave of the industrial revolution, or Industry 4.0 as it makes many industrial fields “smarter” (more efficient). For example:
- Smart supply chain management.
- Smart manufacturing.
- Smart power grids.
- Smart cities.
- Smart farming.
- Connected logistics.
Autonomous cars (and other vehicles)
An “autonomous” means a “self-driving” car or a “driverless” car. Essentially, autonomous cars can drive themselves without the driver having to do anything, like steering, checking blind spots, or changing lanes.
Self-driving cars work through a simple but highly sophisticated system using the Internet of Things and Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence. The driverless car is packed with sensors that monitor everything that is going on the road and around the car.
When these sensors are coupled with an IoT-based technology system, the car can not only use it for driving on its own but also share this information with other IoT-enabled vehicles. For example, a huge amount of information regards traffic, roads, and navigation. When autonomous cars feed each other with live data, they can drive safer and plan the route more efficiently.
Healthcare
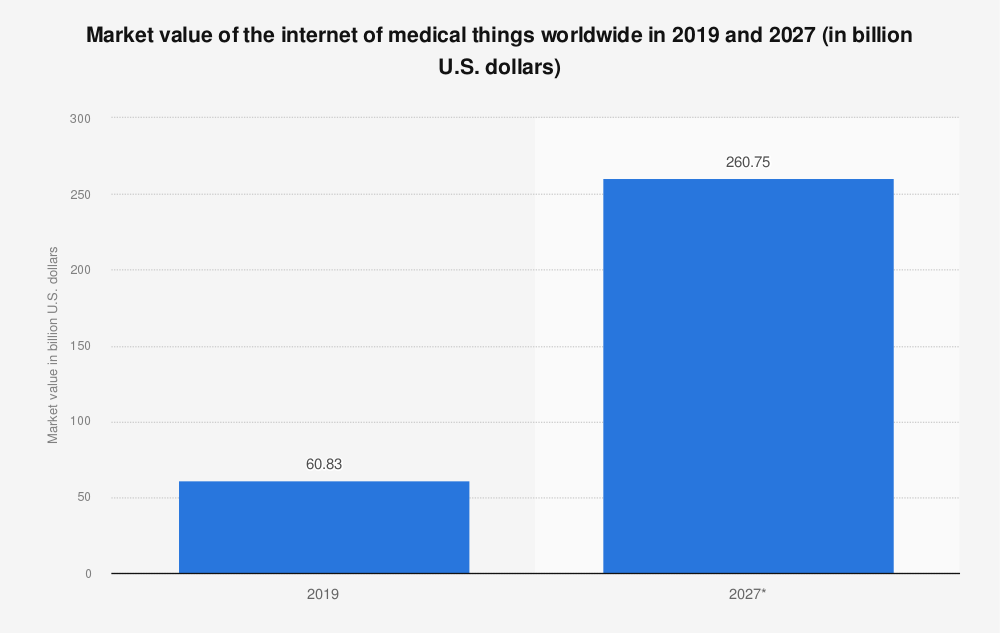
The global Medical Internet of Things (IoMT) market was valued at approximately $61 billion in 2019. By 2027, the market value is expected to reach over $260 billion.
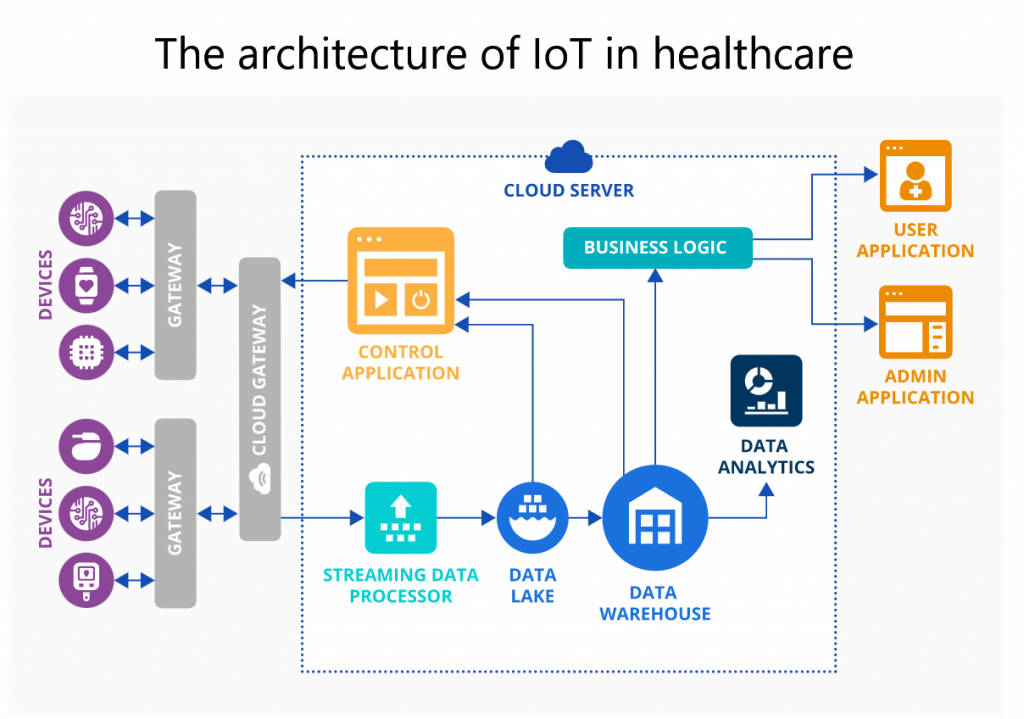
IoMT is popular for remote patient monitoring, hospital asset and medical staff location tracking, and more. It enables uninterrupted real-time monitoring and helps automate routine care delivery operations and administrative tasks and ensures a safe patient stay at the hospital.
In healthcare, the IoT application usually connects a set of medical devices through gateways to a cloud server. The cloud server hosts data storage, processing, and analytics modules, solution business logic, and control applications. The user and admin apps enable patients, medical staff, and other users to access the data and send commands to control apps.
The IoMT also makes its way into digital therapies, known as “digiceuticals,” These therapies use software and data to optimize existing medical interventions. Examples include pills that contain ingestible sensors that tell a doctor when a patient has taken medication, thereby helping to ensure that the patient follows the doctor’s orders.
Other IoT-driven medical interventions include remote surgeries. In 2020, a Chinese medical team has performed a remote radical cystectomy on a patient 3,000 kilometers away with the help of a surgical robot using a low-latency 5G network. Such innovations could allow patients to access the treatment regardless of their location, especially in large countries such as China.
Related:
- Artificial Intelligence For Healthcare: 5 Trends To Watch
- Healthcare Mobile App Development Is a Future For Your Hospital
Retail
IoT devices can collect shopper data and provide personalized recommendations as they move through the store via a mobile app. Shoppers’ experience can be further enhanced by eliminating pain points like products being out of stock. The latest adoption of IoT application in retail include a “scan and send” feature that enables in-store users to check for particular product availability.
With the help of their Internet-enabled phones, shoppers can also buy their groceries without having to interact with cashiers or even a self-checkout. The shoppers simply walk in, pick out their products, and walk out. Amazon calls it a ‘just walk out shopping experience.
Currently, other brands started to follow an autonomous retail experience, so it is slowly but steadily rolling out worldwide. How does it work? The IoT-enabled store works with the mobile app installed on the shoppers’ phones. The sensors inside the store catch which product was picked up (or put back on the shelf). Then, the app adds the products to the “shopping list” and bills the account connected to the app.
Other examples of IoT applications in retail include smart sensors that monitor the food storage temperature. Whenever it becomes abnormal, the system gives an alert. With this simple flow and IoT business applications, sellers can easily decrease the amount of wasted food (or other temperature-sensitive products).
Supply chain and logistics
Challenges such as optimization of supply chains to reduce emissions; monitoring of assets in transit to reduce product spoilage; launching a fleet of fully autonomous vehicles to improve road safety—all can be solved with the help of IoT.
The core innovations in the area of IoT include Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning systems. These smart systems learn and make predictions. Therefore, they can monitor the entire supply chain and identify potential problems based on the variance between current asset movements and planned expectations.
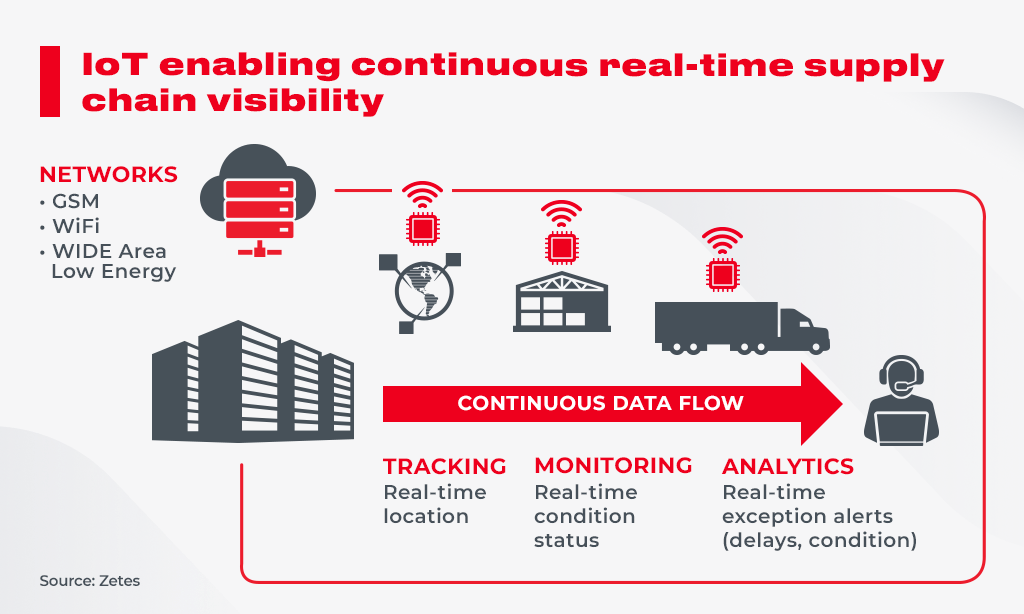
While the goods are in transport, sensors and analytics can notify companies of critical threshold breaches in temperature or humidity that could damage sensitive products like electronics, food, and medicines.
Summary
The transformative potential of IoT applications in business is immense. With the IoT, any company in any field, be it a startup or a global enterprise, could increase its productivity, and customer experience, and decrease operation costs, as well as human resources. All of these are real and achievable with a custom-developed IoT application for devices your users already hold in their hands—mobile phones.
Whether you are a healthcare provider, a supply chain company, a retailer, or any entrepreneur who would like to unlock the power of IoT in their organization, we can help you by developing a custom application that will suit your needs. Contact us to discuss the details of your business idea.



