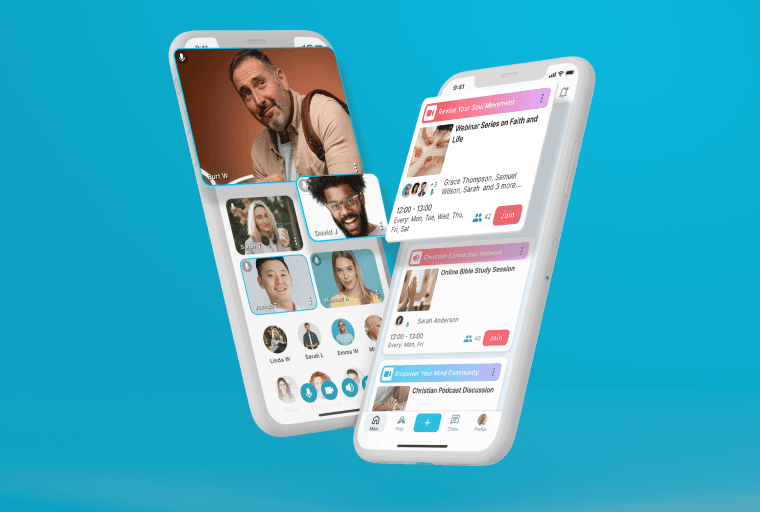
Flutter App Development
Get a highly-performant cross-platform application built with the next-generation Flutter framework. Involve the IDAP team to develop the product of your choice at a fraction of the cost and time.

What is Flutter?
Why Use Flutter?
Why IDAP
Flutter Services
What is Flutter?
Flutter is a free and open-source UI framework created by Google in 2017. It's a powerful and dynamic tool that can bring your app ideas to life in a matter of days. With Flutter, you can build user-friendly and functional apps for Android and iOS using a single codebase.
Why Use Flutter?
01
Single Codebase
Creating apps with a single codebase and seamlessly deploying them across multiple platforms is achievable. There's no need for libraries or dependencies to enable cross-platform functionality. Flutter makes app development faster and more cost-effective
02
Shallow Learning Curve
Creating apps with a single codebase and seamlessly deploying them across multiple platforms is achievable. There's no need for libraries or dependencies to enable cross-platform functionality. Flutter makes app development faster and more cost-effective
03
Better Performance
Creating apps with a single codebase and seamlessly deploying them across multiple platforms is achievable. There's no need for libraries or dependencies to enable cross-platform functionality. Flutter makes app development faster and more cost-effective
04
Not Mobile only
Flutter is a versatile toolkit applicable to Mobile, Web, or Desktop apps. The values it delivers to businesses make it the next emerging trend in app development
Why IDAP
At IDAP Group, we're all about helping businesses achieve their goals with top-of-the-line software solutions. The team of passionate tech enthusiasts is ready to support you at every stage of your journey, from discovery to maintenance. Our solid expertise in Flutter app development allows you to count on top-notch cross-platform applications empowered with a market-proven stack
Flutter App Development Services
Consulting
Share your idea to get a complete understanding and vision of a product on a tight schedule. Our experts will help you dive into your initiative and highlight all strengths and benefits it might deliver for your business.
Migration
Time & material, fixed price, dedicated team, or hybrid? IDAP can get you covered with any outsourcing model. Whether you are a global brand, an international enterprise, or an innovative startup, we’ll adapt our processes to your needs.
App Development
Involve the IDAP team in designing a full-fledged Flutter application cost-effectively. Our experience in this field allow us to deliver best-in-class solutions that exceed business expectations.
Support
Let us care for your Flutter application to keep its competitiveness and efficiency. The IDAP experts can upgrade and enrich the functionality of your app as well as monitor its performance and operation.
Blog
Read all postsMake your Flutter App with IDAP!
We work with clients of all sizes and sectors, from new startup ventures to well-established businesses. Let’s talk about your software needs.
Contacts
Miami, USA
Valencia, Spain
Kyiv, Ukraine
Varna, Bulgaria